Combination use of CD47 Antibodies/Inhibitors with Sorafenib for Liver Cancer Treatment
- Field
- Therapeutic Biologics
- Reference No.
- IP00589
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
- Sorafenib is an FDA-approved drug for treating liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC) but it’s survival benefit was found to be modest due to drug resistance. It was then found that tumor-initiating cells (T-IC) were the reason behind the resistance, where CD47 is the most significant.
- According to FiercePharma.com, the 2012 sales of Sorafenib was US$1.018B, and is projected to reach US$1.463B in 2018.
- Using monoclonal antibody CD47 against cancer has been established, but not the idea of combining it or CD47 inhibitors with sorafenib.
Key Advantages of the Technology
- In vitro test on HCC cell lines showed that combination treatment of sorafenib and anti-CD47 antibody (anti-CD47 Ab) results in a greater sensitivity to sorafenib when compared to treatment using sorafenib or anti-CD47 Ab alone.
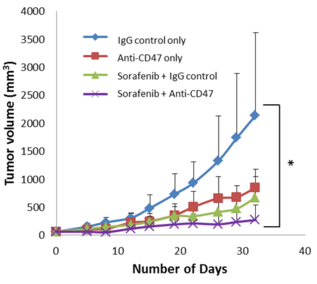
- In vivo test on mice showed that combination treatment of anti-CD47 Ab and sorafenib results in a smaller tumor volume when compared with sole treatment of anti-CD47 Ab or sorafenib. This combination use exerted a synergistic effect, thus maximized suppression of tumors.
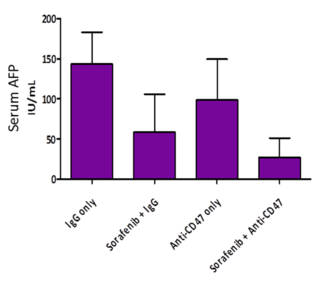
- When co-treated with anti-CD47 Ab and sorafenib, the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a liver T-IC marker, had the greatest reduction.
- Figure 1: Combined effect of anti-CD47 Ab and sorafenib induced maximal suppression of tumors when compared to the control group.
- Journal publication: Hepatology. 2015 Aug;62(2):534-45. doi: 10.1002/hep.27859.
Potential Product and Services
- Therapeutic Regimen for HCC
- Combination Treatment for HCC
- Methods increasing sensitivity of liver cancer cells to sorafenib
Development Status
Patents
- Patent application: US Patent application No.14/856,137;
IP Status
- Patent application submitted