Fecal Microbial Biomarkers for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Field
- Therapeutic Biologics
- Patent
- IP01037
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) refers to a wide range of liver conditions caused by the deposition of fat in liver. The cause of NAFLD is not clear, and the NAFLD is one of the most common diseases in the United States and Western Countries.
- The prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is rising due to rise in prevalence of diabetes and obesity which are the known risk factors. According to the survey, out 20-30% of the general population in the western world suffer from NAFLD.
- The global NAFLD market is estimated to be valued at US$17.43 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach at a market value of US$62.06 billion by 2031 with CAGR at 13.35% and US would be the largest market.
Key Advantages of the Technology
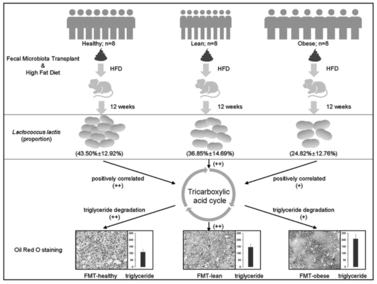
- The result indicated the gut microbiome for NAFLD patients and healthy individuals are different, especially a specific bacterium, , is significantly decreased in the obese NAFLD patents.
- Mice colonized with healthy microbiota had a significantly lower intrahepatic lipid accumulation than those with obese NAFLD microbiota. This suggested that changing gut microbiota condition may act as one of the biomarker for NAFLD risk evaluation and therapeutic target for treating/improving the NAFLD.
- Microbiome analysis confirmed a significantly higher mean abundance of in FMT-Healthy mice than FMT-Obese mice. This suggested that may be one of the key bacteria that contribute to the effect.
Benefits
- Diagnostic tool to evaluate the risk for developing NAFLD
- Probiotic dietary supplement/therapeutic candidate to prevent/improve the NAFLD condition
Development Status and IP Strength
Patents
- US regular patent application
IP Status
- Patent application submitted