Immuno-Oncolytic Modified Vaccinia Tian Tan Virus and Methods of Treating Cancer
- Field
- Therapeutic Biologics
- Reference No.
- IP00729
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
Mesothelioma is an asbestos-associated malignant form of cancer, which often has a poor prognosis in humans after disease onset.
- The current standard of care for this life-threatening malignancy only achieves suboptimal improvements in patient survival.
- Harnessing the host immune system to eradicate malignant cells has become a clinical strategy in cancer immunotherapy.
- However, although immune checkpoint inhibitors have improved the therapeutic efficacy in certain cancers, their effects are unsatisfactory in patients with mesothelioma.
- Novel strategies, therefore, are needed for treating mesothelioma.
Key Advantages of the Technology
- The current invention describes an immune-oncolytic method by combining intratumoral administration of oncolytic modified vaccinia Tian Tan (MVTT) virus and depletion of myeloid-derived immunosuppressive cells (MDSCs) to induce protective T cell immune responses that exhibited dose-dependent effects in regression of solid tumors such as mesothelioma (AB1) and melanoma (B16F10).
-
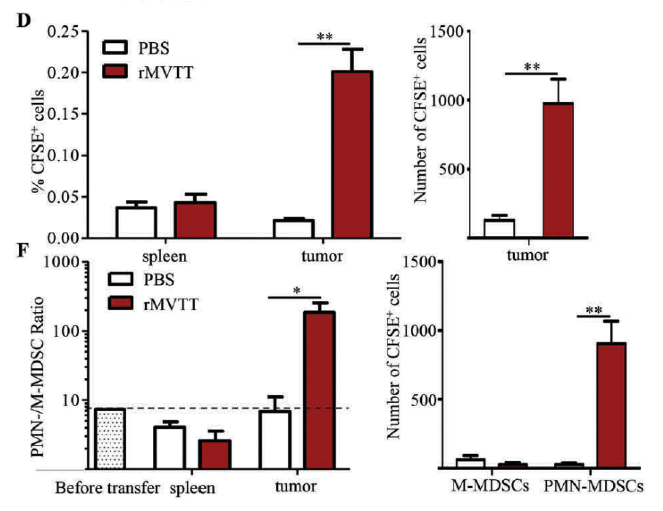
Figure 1D: Frequencies (left panel) and absolute numbers (right panel) of CFSE-labelled total MDSCs in both spleen and tumor 24 hours after treatment. Each mouse received 50 μl PBS or rMVTT (1 × 107 PFU).F: Changes in the ratio of the PMN-MDSC proportion to the M-MDSC proportion were analyzed (left panel). PMN-/M-MDSC ratio measured before adoptive transfer was shown as baseline. Changes in the absolute numbers of M-MDSCs and PMN-MDSCs in the tumor are shown (right panel)
Benefits
- Induces protective antitumor T cell responses, which are normally suppressed or even absent under the tumor environment. Consequently, it will enhance therapeutic efficacy of oncolytic therapy.
- MVTT-mediated oncolytic effects resulted in localized chemokine production that recruited MDSCs into tumor microenvironments to suppress the induction of anti-cancer specific T cell immunity.
- Depletion of MDSCs especially PMN-MDSCs during MVTT treatment is able to restore potent antitumor T cell immunity by eliciting cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses, which are required for the clearance of mesothelioma.
Potential Product and Services
- Induce protective anti-cancer T cell immunity for clinical application.
Development Status
Patents
- US Provisional Application No. 62/ 687531 filed on 20-Jun-2018
IP Status
- Patent application submitted