Novel Vδ2-T Cells Derived Exosomes Treatment for Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Associated Cancers
- Field
- Therapeutic Biologics
- Reference No.
- IP00892
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
Background
-
The global cancer therapeutics market is expected to grow from $128.1 billion in 2018 to $182.0 billion by 2023 at a CAGR of 7.3%. EBV associated cancer accounts for 1-2% of all cancers.
-
Current treatment options for EBV-associated tumors are very limited with remarkable unwanted off-target toxicities
Technology Overview
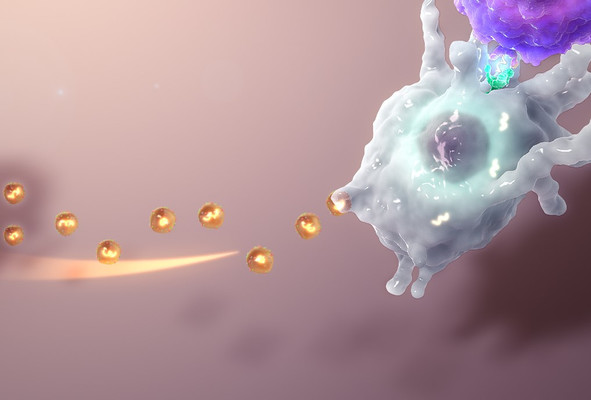
The exosomes demonstrate an EBV-associated tumor specific tropism, ability to distinguish normal and infected B cells and capacity to trigger both tumor cell apoptosis and stimulate anti-tumor T cell activities.
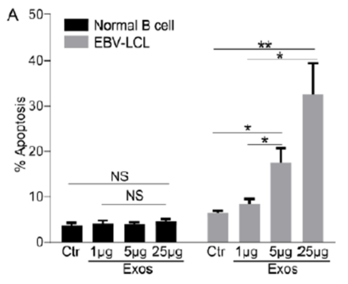
Figure 1. Graph showing % apoptosis in autologous normal B cells and EBV-LCL after exosome treatment.
Stage of Development
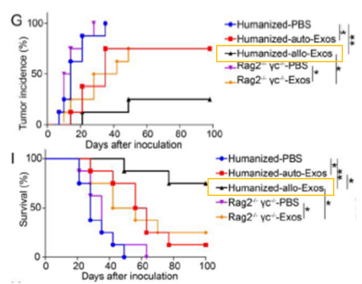
Verified in EBV-associated B-cell lymphoma model
Key Advantages of the Technology
- Potential to be the first exosome therapy for the treatment of EBV-associated cancer
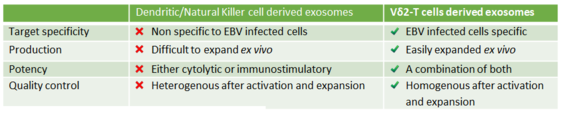
- Superiority over both conventional treatments, novel cell based treatments and other immune cell derived exosomes
Potential Product and Services
Novel therapeutic for the treatment of EBV associated cancers
Development Status
Patents
- US provisional patent application No. 62916430
IP Status
- Patent application submitted